Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Ultimate Power Roles Revealed
Ever wondered who keeps the digital backbone of a company running smoothly? Meet the systems manager—the unsung hero of modern IT operations. With tech evolving at lightning speed, this role has never been more critical—or more complex.
What Is a Systems Manager?

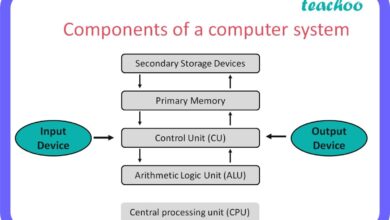
A systems manager is a key IT professional responsible for overseeing the design, implementation, and maintenance of computer systems within an organization. This role sits at the intersection of technology and business strategy, ensuring that hardware, software, networks, and data centers operate efficiently and securely.
Core Definition and Scope
The term ‘systems manager’ can vary in meaning depending on the industry and company size. In large enterprises, it may refer to someone managing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, while in tech startups, the role might encompass cloud infrastructure and DevOps practices. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, systems managers plan, coordinate, and direct research and development activities in an organization’s IT department.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Responsible for system architecture and integration
- Ensures alignment between IT goals and business objectives
- Manages budgets, timelines, and vendor relationships
“A systems manager isn’t just a tech expert—they’re a strategic leader who translates business needs into technological solutions.” — TechLeaders Journal, 2023
Evolution of the Role Over Time
The role of systems manager has evolved dramatically since the 1980s. Originally focused on mainframe administration and data processing, today’s systems managers deal with cloud computing, cybersecurity, AI integration, and hybrid work environments. The rise of digital transformation initiatives has elevated this position from a back-office function to a C-suite advisory role.
- 1980s–1990s: Focused on internal networks and server maintenance
- 2000s: Emergence of network security and helpdesk oversight
- 2010s–Present: Cloud migration, automation, and compliance leadership
Key Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
The day-to-day duties of a systems manager are both broad and deep. They must balance technical expertise with leadership skills to ensure seamless operations across all IT systems.
System Design and Implementation
One of the primary responsibilities of a systems manager is designing scalable and secure IT infrastructures. This includes selecting appropriate hardware and software, planning network topologies, and overseeing deployment processes. Whether rolling out a new CRM platform or migrating legacy systems to the cloud, the systems manager ensures everything is integrated smoothly.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Conducts needs assessments and feasibility studies
- Creates technical specifications and architecture blueprints
- Coordinates with developers, vendors, and stakeholders during rollout
For example, when a financial institution upgrades its transaction processing system, the systems manager leads the project from concept to execution, ensuring zero downtime and regulatory compliance.
Maintenance, Monitoring, and Optimization
Once systems are live, ongoing maintenance becomes crucial. Systems managers use monitoring tools like Nagios, SolarWinds, or Datadog to track performance metrics such as uptime, latency, and resource utilization. Proactive maintenance helps prevent outages and optimize efficiency.
- Schedules routine updates and patches
- Performs root cause analysis on system failures
- Implements performance tuning and load balancing
“Prevention is better than cure—especially in IT. A good systems manager spends more time preventing problems than fixing them.” — CIO Magazine, 2022
Essential Skills for a Successful Systems Manager
To thrive in this multifaceted role, a systems manager must possess a unique blend of technical, analytical, and interpersonal skills.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Technical Proficiency
Deep knowledge of operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS), virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V), and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) is non-negotiable. Additionally, familiarity with scripting languages (Python, PowerShell), database management (SQL, NoSQL), and containerization (Docker, Kubernetes) is increasingly important.
- Mastery of network protocols (TCP/IP, DNS, DHCP)
- Experience with system automation and configuration management (Ansible, Puppet)
- Understanding of cybersecurity frameworks (NIST, ISO 27001)
According to a 2023 report by Gartner, 78% of high-performing IT teams list cloud and automation skills as top priorities for systems managers.
Leadership and Communication Abilities
While technical skills get you in the door, leadership keeps you in the room. Systems managers often lead teams of engineers, coordinate cross-functional projects, and present findings to executives. Strong communication—both written and verbal—is essential for translating complex technical issues into business terms.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Ability to delegate tasks and mentor junior staff
- Facilitating meetings with stakeholders from non-technical departments
- Negotiating contracts with third-party vendors
“The best systems managers aren’t just coders or admins—they’re translators between tech and business.” — Harvard Business Review, 2021
Systems Manager vs. Other IT Roles
It’s easy to confuse the systems manager with other IT positions like network administrators, IT directors, or DevOps engineers. While there’s overlap, each role has distinct responsibilities and scopes.
Differences from Network Administrators
Network administrators focus primarily on maintaining network infrastructure—routers, switches, firewalls, and connectivity. In contrast, systems managers have a broader scope that includes servers, storage, applications, and overall system integration. A network admin might troubleshoot a slow LAN connection; a systems manager would assess whether the entire IT ecosystem supports current business demands.
- Network admin: Day-to-day network health
- Systems manager: Strategic system planning and scalability
- Collaboration often occurs during infrastructure upgrades
Comparison with IT Directors and CIOs
IT directors and Chief Information Officers (CIOs) operate at a higher strategic level, focusing on long-term vision, budgeting, and organizational policy. Systems managers typically report to these leaders and execute their strategies. However, in smaller organizations, the systems manager may wear multiple hats, performing both tactical and strategic functions.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- IT Director: Oversees entire IT department
- Systems Manager: Manages specific systems and technical teams
- CIO: Aligns IT with corporate strategy and innovation
For instance, while the CIO decides to adopt AI-driven analytics, the systems manager selects the right platforms, ensures data integrity, and integrates the solution into existing workflows.
Tools and Technologies Used by Systems Managers
Modern systems managers rely on a robust toolkit to monitor, manage, and secure complex IT environments.
Monitoring and Management Platforms
Tools like SolarWinds, Zabbix, and PagerDuty allow systems managers to gain real-time visibility into system performance. These platforms provide dashboards, alerting systems, and historical reporting to support proactive maintenance.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Real-time server and application monitoring
- Automated incident response and escalation
- Capacity planning based on usage trends
Cloud and Virtualization Solutions
With over 90% of enterprises using cloud services, systems managers must be proficient in platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). They use these environments to deploy scalable applications, manage storage, and enforce security policies.
- Provisioning virtual machines and containers
- Managing identity and access controls (IAM)
- Implementing backup and disaster recovery strategies
“Cloud fluency is no longer optional for systems managers—it’s a baseline requirement.” — Forbes Technology Council, 2023
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers Today
Despite the rewards, the role comes with significant challenges that test even the most experienced professionals.
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Protection
Ransomware attacks, phishing campaigns, and insider threats are constant concerns. Systems managers must implement multi-layered security strategies, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), encryption, and employee training programs. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA adds another layer of complexity.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing
- Enforcing least-privilege access models
- Developing and testing incident response plans
A 2023 report by Cisco found that 68% of organizations experienced a significant cyberattack in the past year—making the systems manager’s role in defense more vital than ever.
Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Change
Technology evolves at breakneck speed. New frameworks, tools, and best practices emerge constantly. Systems managers must engage in continuous learning through certifications (e.g., CISSP, AWS Certified Solutions Architect), industry conferences, and peer networks to stay current.
- Adapting to AI and machine learning integrations
- Managing hybrid and remote work infrastructures
- Addressing sustainability and energy efficiency in data centers
“The only constant in IT is change. A systems manager who stops learning is already behind.” — Wired, 2022
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities for Systems Managers
The career trajectory for a systems manager is both diverse and promising, offering multiple pathways for growth and specialization.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Typical Entry Points and Progression
Most systems managers begin their careers in technical roles such as system administrators, network engineers, or software developers. With experience and demonstrated leadership, they transition into management positions. A bachelor’s degree in computer science, information systems, or a related field is typically required, though many hold advanced degrees or certifications.
- Entry-level: System Administrator, IT Support Specialist
- Mid-level: Senior Systems Engineer, IT Team Lead
- Senior-level: Systems Manager, IT Operations Manager
Progression often depends on a combination of technical expertise, project success, and soft skills like communication and strategic thinking.
Advanced Roles and Executive Transitions
From the systems manager position, professionals can advance to roles such as IT Director, Chief Technology Officer (CTO), or Chief Information Officer (CIO). These executive positions involve broader organizational leadership, budget oversight, and digital transformation strategy.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- CTO: Focuses on technology innovation and R&D
- CIO: Aligns IT with business goals and regulatory compliance
- IT Director: Manages department operations and staffing
Some systems managers also pivot into consulting, entrepreneurship, or specialize in niche areas like cybersecurity or cloud architecture.
Industry-Specific Applications of Systems Management
The role of a systems manager varies significantly across industries, each with unique demands and regulatory landscapes.
Healthcare and HIPAA Compliance
In healthcare, systems managers ensure that electronic health record (EHR) systems comply with HIPAA regulations. This involves securing patient data, managing access controls, and conducting regular audits. Downtime in medical systems can be life-threatening, so reliability and disaster recovery are paramount.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Implementing encrypted data storage and transmission
- Ensuring 99.99% uptime for critical systems
- Training staff on data privacy protocols
Organizations like the Mayo Clinic rely heavily on skilled systems managers to maintain secure, efficient IT operations across multiple campuses.
Finance and Regulatory Systems Oversight
Financial institutions require systems managers to oversee transaction processing, fraud detection systems, and compliance with regulations like SOX and PCI-DSS. High-frequency trading platforms, for example, demand ultra-low latency and fault-tolerant architectures.
- Monitoring real-time transaction integrity
- Managing audit trails and logging mechanisms
- Coordinating with compliance officers and auditors
“In finance, a millisecond delay can cost millions. Systems managers are the guardians of speed and accuracy.” — Wall Street Journal, 2023
What does a systems manager do?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
A systems manager oversees the design, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. They ensure that computer systems, networks, and software operate efficiently, securely, and in alignment with business goals. Their responsibilities include system upgrades, performance monitoring, cybersecurity, team leadership, and strategic planning.
How do I become a systems manager?
To become a systems manager, start with a degree in computer science or information technology. Gain hands-on experience in roles like system administrator or network engineer. Pursue certifications such as CompTIA, CISSP, or cloud-specific credentials (AWS, Azure). Develop leadership and communication skills, and seek opportunities to lead projects or teams.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
What skills are essential for a systems manager?
Essential skills include technical proficiency in operating systems, networking, cloud platforms, and cybersecurity; strong problem-solving abilities; leadership and team management; excellent communication; and strategic thinking. Familiarity with automation tools and scripting languages is increasingly important.
Is systems manager a high-demand job?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Yes, systems manager is a high-demand job. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 10% growth in employment for computer and information systems managers from 2021 to 2031, faster than average. Demand is driven by cloud computing, cybersecurity needs, and digital transformation across industries.
What is the average salary for a systems manager?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $159,010 as of May 2022. Salaries vary by industry, location, and experience, with top earners in finance and tech sectors exceeding $200,000 annually.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The role of a systems manager is more than just technical oversight—it’s about bridging the gap between technology and business success. From designing resilient infrastructures to leading teams through digital transformation, systems managers are pivotal in today’s data-driven world. As cyber threats grow and technology accelerates, their importance will only increase. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or looking to hire a top-tier professional, understanding the depth and breadth of this role is essential for thriving in the modern digital landscape.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: